How to Write an Effective Prompt for AI: Getting Better Images, Charts, Data, and Tone
In the world of generative AI, the quality of your output is only as good as the quality of your input. Whether you’re prompting ChatGPT to generate images, graphs, or structured reports, your ability to write an effective prompt directly determines the usefulness, creativity, and accuracy of the results. Think of a prompt as your instruction manual — the more clear, specific, and well-structured it is, the more likely you are to get exactly what you envision.
Here’s a breakdown of how to craft powerful prompts, specifically tailored for image generation, data visualization, and tone customization.
1. Writing Prompts for the Best Image Results
Image generation models (like DALL·E, Midjourney, or Stable Diffusion) thrive on specific, visual, and layeredprompts. To get the best results:
Use These Elements in Your Image Prompt:
- Subject: What should be the focal point? (e.g., “a futuristic cityscape”)
- Style: What art style? (e.g., “in the style of cyberpunk digital painting”)
- Mood: What emotional tone or atmosphere? (e.g., “moody, rainy, cinematic lighting”)
- Composition: How should it be framed? (e.g., “wide-angle view from above”)
- Color Palette: Any dominant hues? (e.g., “neon blues and purples”)
- Detail Level: Do you want realism or abstraction? (e.g., “ultra-detailed, 4k resolution”)
Example of a Weak Prompt:
“Draw a robot”
Example of a Strong Prompt:
“A sleek humanoid robot standing in a neon-lit alley at night, ultra-detailed, in the style of Blade Runner, reflective chrome body, misty atmosphere, cinematic 35mm film grain”
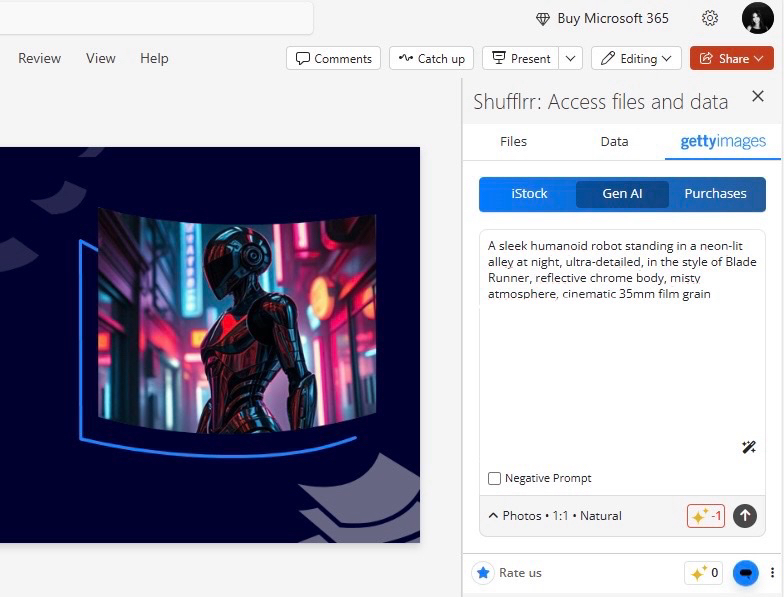
The second prompt guides the AI with clarity and intent, giving it more context to work with.
2. Prompting for Charts and Data Visualization
If you want AI to generate charts or graphs, especially with tools like Python (Matplotlib, Seaborn), Excel, or even in documentation like Word or Notion, precision is key. You need to define:
Key Elements for Data Prompts:
- What type of chart (e.g., bar, line, pie, scatter)
- Data source or format (either real data or a structure like CSV, JSON, or tables)
- X-axis and Y-axis labels (time, categories, values, etc.)
- Purpose (comparison, trend, correlation, etc.)
Example:
“Generate a line chart comparing monthly sales for three products (Product A, B, and C) over a 12-month period. Include labeled axes, a legend, and a title. Output the code using Matplotlib.”
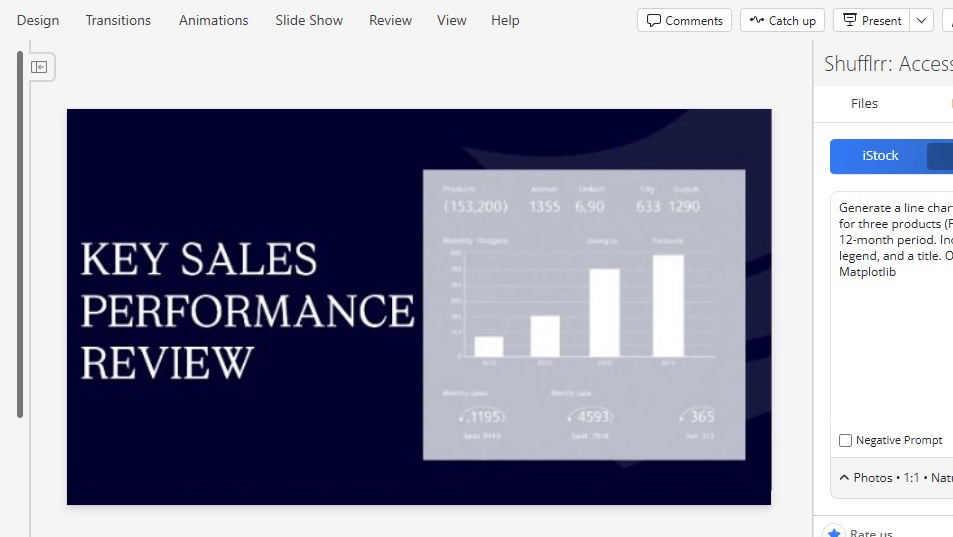
To ensure accuracy, either provide your actual data or request that the AI simulate reasonable values.
3. Prompting for Structured Data and Tables
Want a clean, tabulated output? Use cues like:
- “Give the result in a table”
- “Create a CSV format”
- “List as a markdown table”
Example:
“Create a comparison table of electric vehicles under $50,000 showing model name, range per charge, and charging time. Format as a markdown table.”
This ensures the response is usable across platforms (Markdown, Excel, HTML).
4. Setting the Right Tone in Your Prompt
Tone is everything when you’re asking AI to draft content — emails, articles, ads, or reports. Whether you want it formal, casual, humorous, persuasive, or academic, you must say so clearly.
🎙Tone Cues to Include:
- “Use a professional tone”
- “Make it sound like a conversation between friends”
- “Adopt a motivational and inspiring voice”
- “Use humor like The Onion”
- “Write like an academic journal article”
Example:
“Write a 300-word blog post explaining blockchain to high school students in a fun, conversational tone, using analogies and no technical jargon.”
Tone + audience + format = maximum precision.
5. Advanced Tips for Better Prompts
- Use modifiers: Words like “realistic,” “vintage,” “hyper-detailed,” “low-poly,” “minimalist” sharpen your prompt.
- Chain of thought prompting: Ask the AI to think step-by-step to solve complex problems.
- Set constraints: “Limit response to 150 words” or “Only list 5 examples”
- Give context: “Assume you are a marketing executive…” or “Pretend you are teaching a 5-year-old…”
6. Prompt Templates You Can Steal
For Image:
“A [subject] in a [location], in the style of [artist/style], with [color palette], [mood], and [lighting details]”
For Chart:
“Generate a [chart type] comparing [X] and [Y] over [time frame], including [labels, title, legend]. Use sample data if needed.”
For Tone:
“Write a [content type] in a [tone] for a [audience], focusing on [topic] with [desired length or format]”
Final Thoughts
Prompt engineering is becoming a vital skill — like coding for creatives or briefing for marketers. You don’t need to be a tech wizard. You just need to be clear, specific, and imaginative.
Whether you’re creating art, data dashboards, or business content, mastering the art of prompting will unlock the full potential of AI — giving you faster, smarter, and more creative results.
Try it now: Go back to your last vague prompt and rewrite it using the formulas above — you’ll be amazed at the difference.